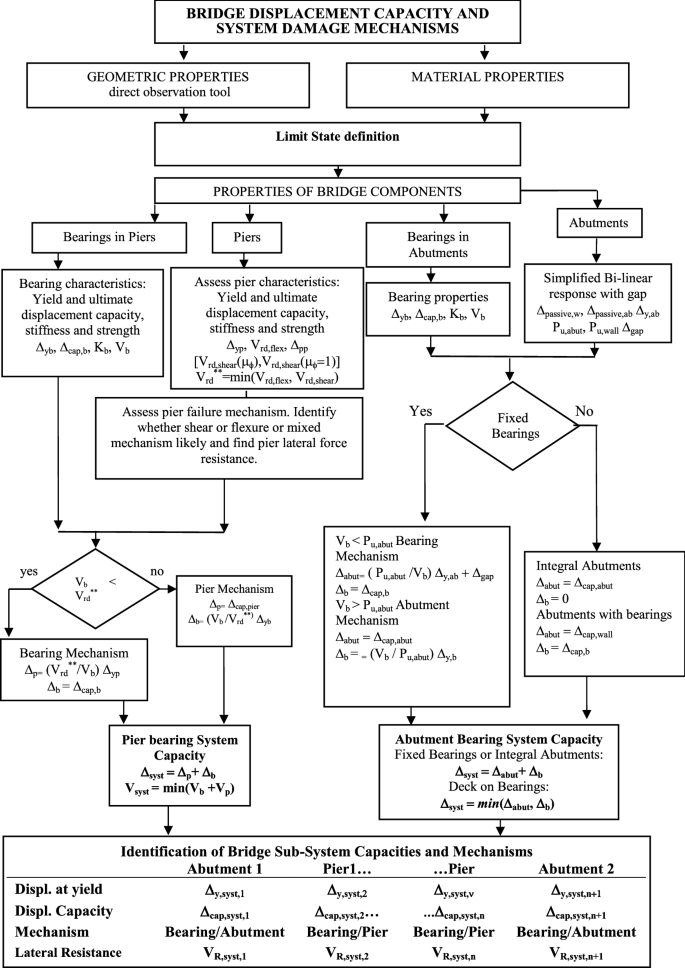
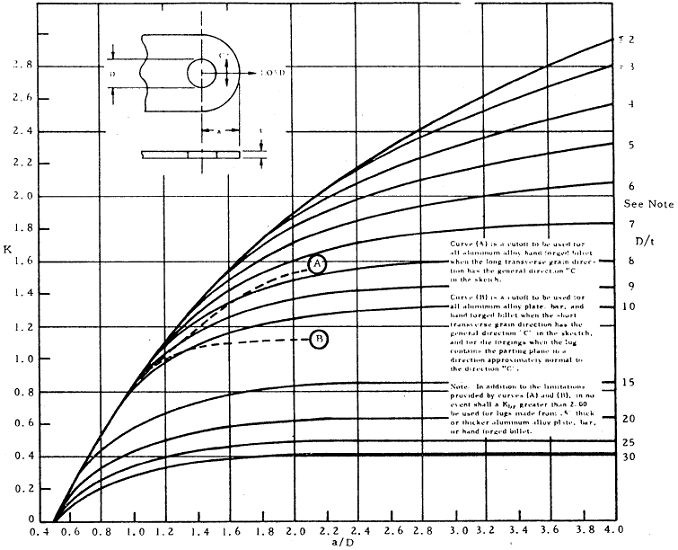
The bearing stresses and loads for lug failure involving bearing shear tearout or hoop tension in the region forward of the net section in figure 9 1 are determined from the equations below with an allowable load coefficient k determined from figures 9 2 and 9 3 for values of e d less than 1 5 lug failures are likely to involve shear.
Solve for bearing and shear stress of door hinge.
Almost any length width thickness or material.
Many load bearing points equal to the number of knuckles per leaf.
Shear stress ave n mm 2 lbs in 2 f applied force n lbs π pi or 3 14157 r radius mm in d diameter mm in bearing stress equation.
Shear stress equation double shear.
Mass or weight of the test port based on the category that you want to achieve.
Uniform strength throughout the entire length.
See barrett for more details on estimates of bearing allowables.
Shear stress normal stress is a result of load applied perpendicular to a member.
Shear stress forces parallel to the area resisting the force cause shearing stress.
Use of two hinges one load bearing in the case of concealed hinges both hinges are load bearing.
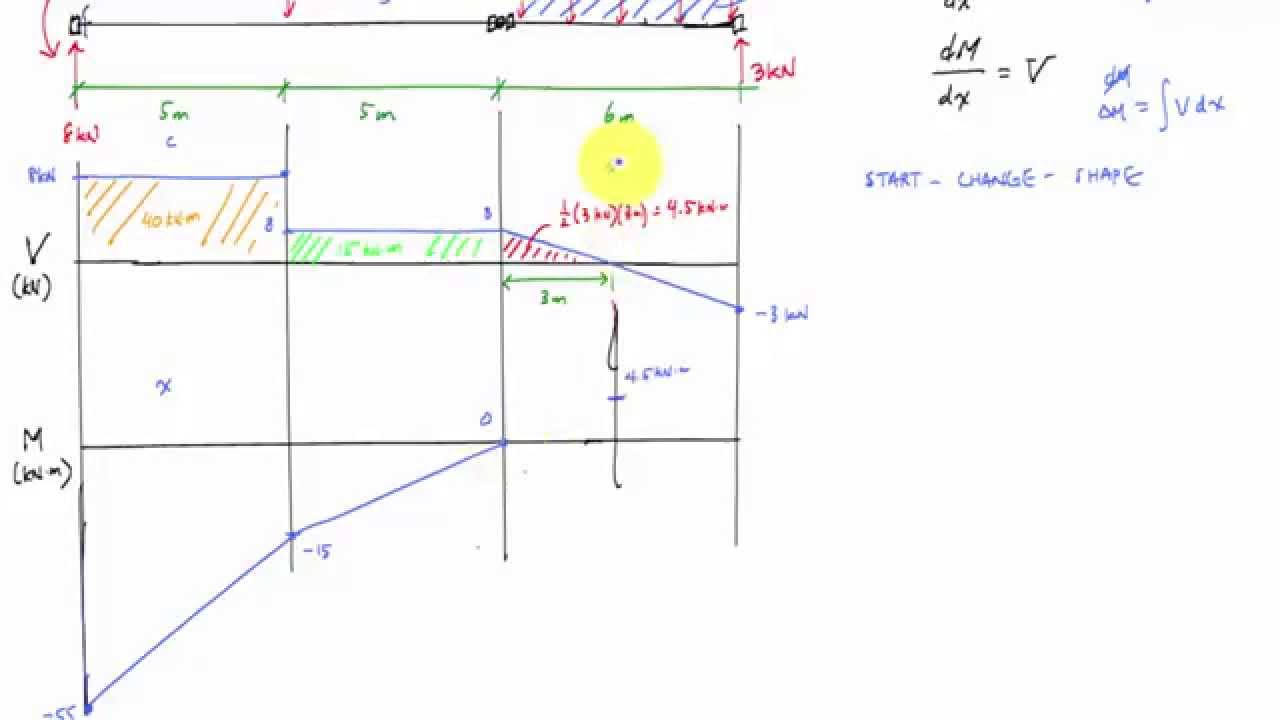
Looking again at figure one it can be seen that both bending and shear stresses will develop.
200 000 opening cycles for use on doors.
Most structures need to be designed for both normal and shear stress limits.
I have always assumed that it is a double shear problem.
Shear stress however results when a load is applied parallel to an area.
Easier and more accurate alignment than two or more butt hinges.
Shear stress average applied force area or shear stress ave f 2 π r 2 or shear stress ave 4f 2 π d 2 where.
9 3 1 lug bearing strength under uniform axial load.
Bearing area stress for t plate.
In a previous lesson we have learned about how a bending moment causes a normal stress this normal stress often dominates the design criteria for beam strength but as beams become short and thick a transverse shear stress.
The bearing yield strength can typically by estimated as 1 5 s ty.
As we learned while creating shear and moment diagrams there is a shear force and a bending moment acting along the length of a beam experiencing a transverse load.
Shear loading on plate.
It differs to tensile and compressive stresses which are caused by forces perpendicular to the area on which they act.
This is very interesting.
In addition to normal stress that was covered in the previous section shear stress is an important form of stress that needs to be understood and calculated.
A standard door 2000 mm h x 1000 mm w and a distance of 1540 mm between hinges.
Like in bending stress shear stress will vary across the cross sectional area.